R-Values
What is an R-Value?
The "R-value" refers to the thermal resistance of a material. It measures how well a material can resist the flow of heat through it. The higher the R-value, the greater the material's resistance to heat transfer.
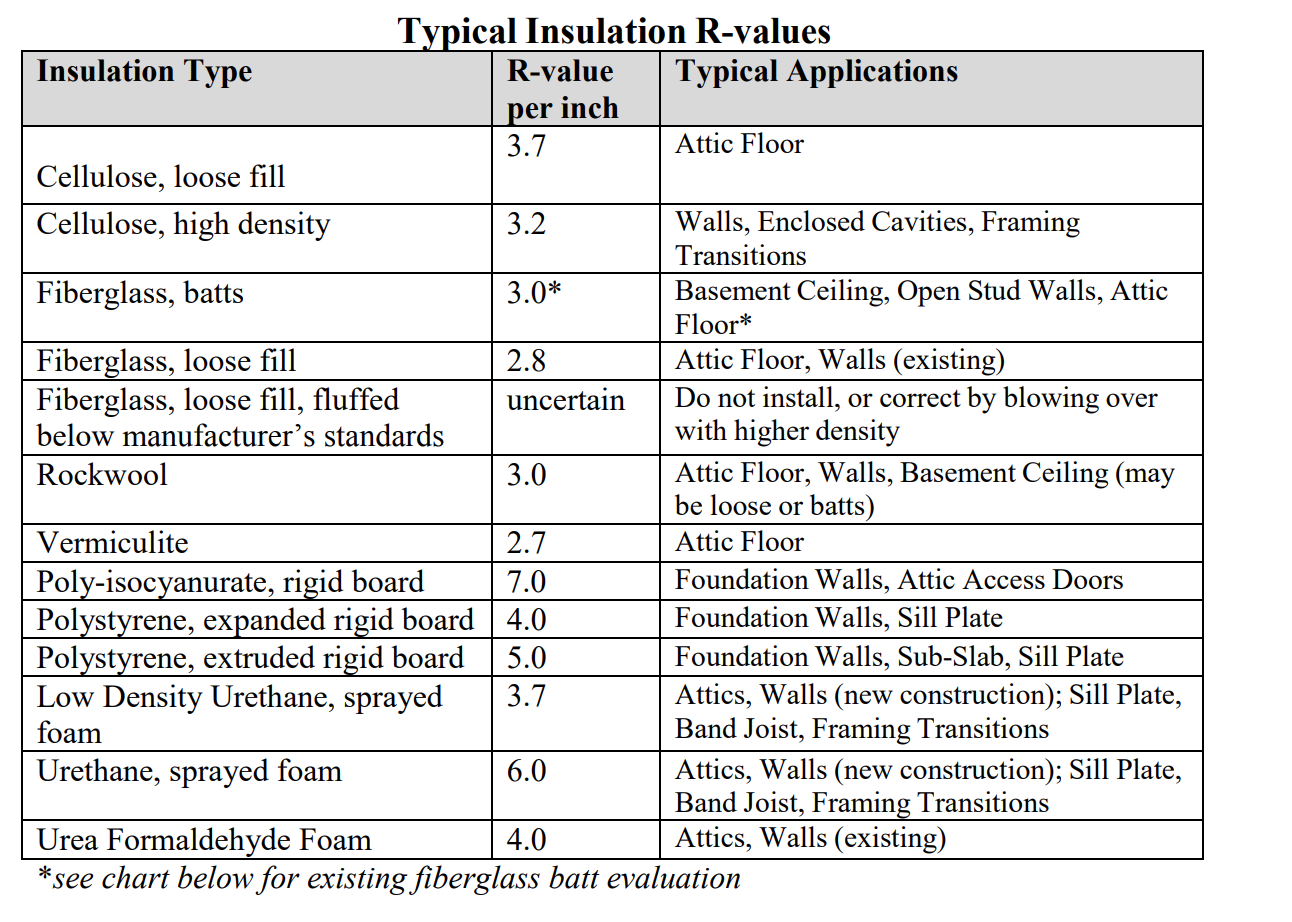
Check out the chart below to correlate with the different insulation types!
In the context of home insulation, the R-value is used to determine the effectiveness of insulation materials in reducing heat flow. Insulation with a higher R-value provides better thermal resistance and can help keep your home more comfortable and energy-efficient.
Different insulation materials have varying R-values per inch of thickness. For example, fiberglass batt insulation typically has an R-value of around 3.1 to 3.4 per inch, while rigid foam insulation can have higher R-values ranging from 4 to 7 per inch. The recommended R-value for insulation in a specific area depends on factors such as climate, local building codes, and the desired level of energy efficiency.
When selecting insulation for your home, it's important to consider the recommended R-values for your region and the specific areas you're insulating, such as walls, ceilings, or floors. Proper insulation with the appropriate R-value can help reduce heat loss or gain, improve energy efficiency, and enhance overall home comfort.
What R- Values Should Specific Spots in your house be at?
In Maryland, the recommended R-value for insulation can vary depending on the specific area of your home and the climate zone in which you reside. The Department of Energy (DOE) provides general guidelines for recommended R-values based on climate zones.
Maryland is predominantly located in Climate Zone 4, with some areas falling into Climate Zone 3. Here are the DOE's general recommendations for insulation R-values in these climate zones:
Attic: The recommended R-value for attic insulation in Maryland's Climate Zones 3 and 4 is typically between R-38 and R-60. This can be achieved with a combination of insulation types, such as fiberglass batts or blown-in insulation.
Walls: For above-grade walls, the recommended R-value in Climate Zones 3 and 4 is typically between R-13 and R-21. This can be achieved with insulation options like fiberglass batts, rigid foam boards, or spray foam insulation.
Floors: For above-grade floors, the recommended R-value in Climate Zones 3 and 4 is generally between R-13 and R-30. Insulation options for floors include fiberglass batts, rigid foam boards, or spray foam insulation.
It's important to note that these are general recommendations, and specific R-values may vary based on factors such as the age of your home, local building codes, and personal preferences. Consulting with a professional energy auditor or insulation contractor can provide more tailored recommendations based on your specific home and needs.
Remember, higher R-values generally provide better insulation performance and energy efficiency. However, it's essential to strike a balance between insulation levels and cost-effectiveness, taking into account factors such as your heating and cooling system, local climate, and energy-saving goals. Also, keep in mind that these are minimum requirements.
Before choosing any insulation, it is recommended to consult with Smart Energy Professionals first so we can assess your specific needs and provide guidance on the most suitable insulation solution for your project. Schedule an energy audit today or give us a call if you have any questions!